Google Changed Its Definition of ‘Bloodbath’ After Trump Used It in a Speech?
Google “changed its definition” of “bloodbath” to push an anti-Donald Trump agenda after he uttered the word at a campaign rally on March 16, 2024.
On March 16, 2024, former U.S. President Donald Trump said: “Now, if I don’t get elected, it’s going to be a bloodbath for the whole — that’s gonna be the least of it. It’s going to be a bloodbath for the country.” His remark at a campaign rally in Dayton, Ohio, sparked controversy on social media. As Snopes reported on March 17, 2024, its context suggested Trump was predicting an “economic bloodbath” for the country, not a literal one, if he loses the 2024 presidential election.
Five days later, on March 21, 2024, a rumor went viral on X (formerly Twitter), alleging that Google intentionally changed “its definition” of “bloodbath” to push an anti-Trump narrative. This claim is not only false, as we’ll demonstrate below, but based on a complete ignorance of how the search engine’s “dictionary boxes” work. But that didn’t keep the rumor from going viral.
“HOLY S***. Google just quietly changed its search results for ‘bloodbath definition’,” the most viral post on the topic read, reaching over 35 million views as of this writing. The post featured a collage of two screenshots supposedly proving Google tampered with the search results for “bloodbath” between March 17, 2024, and March 21, 2024.
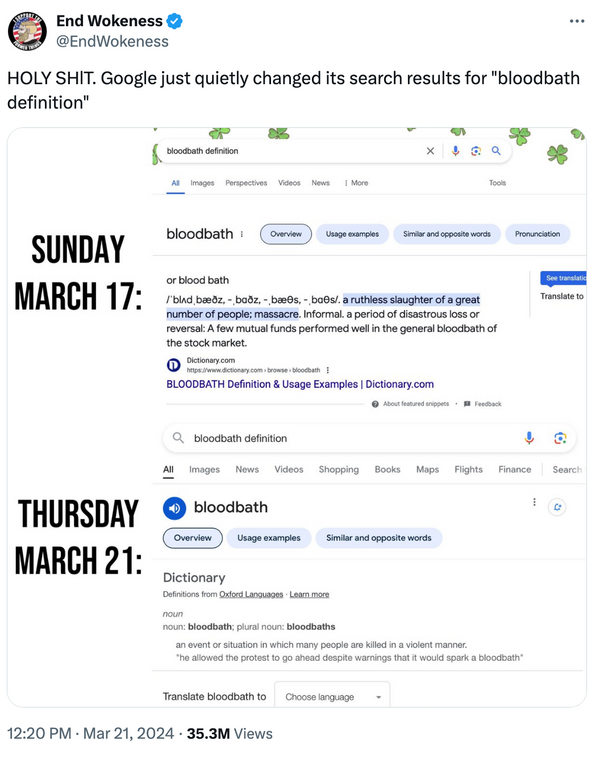
(X user @EndWokeness)
“Definition changed from how it was 4 days ago. Changed to remove the financial example, to ensure Trump’s speech can always be taken out of context. Re-writing the meaning of words in real time,” one Reddit user commented. Even Elon Musk, the owner of X, went all-in on the conspiracy theory. “Google is deeply infected with the woke mind virus” Musk wrote in an X repost of the above-mentioned collage to his 178 million followers.
How ‘Dictionary Boxes’ on Google Really Work
According to a Google Search Help article titled “Dictionary boxes on Google,” these so-called “dictionary boxes” display definitions from third-party sources. It emphasized that “Google doesn’t create, write, or modify definitions” and “dictionary results don’t reflect the opinions of Google” (emphasis ours):
When you search on Google, you might find dictionary boxes if our systems decide it would be useful and relevant. Dictionary boxes show definitions from third-party expert sources and might include related images, pronunciations, translations, and other information.
Tip: You’re likely to get a Dictionary result when you start your search with “Define” or “What’s the meaning of.”
Where info in Dictionary boxes comes from
Important: Dictionary boxes always include definitions but might not include all other features.
Definitions
Google doesn’t create, write, or modify definitions. Dictionary results don’t reflect the opinions of Google.
We license definitions, which include examples, similar and opposite words, and origins, from third-party experts who compile dictionaries.
Tip: At the top of a Dictionary box, you can usually find the provider of the definition.
We reached out to Google directly to ask for its response to the claim that the definitions were purposely changed. “This allegation is categorically false,” a spokesperson told us. “These definitions come from dictionaries, not from Google. We don’t create, write, or modify definitions, and we don’t manually decide which results appear. Both of these definitions have shown up for this search and related searches in recent days. ”
This confirms what various social media users had pointed out: The viral image didn’t show an individual dictionary entry that had changed; it showed definitions from two different sources, Dictionary.com website and Oxford Languages (see image below).
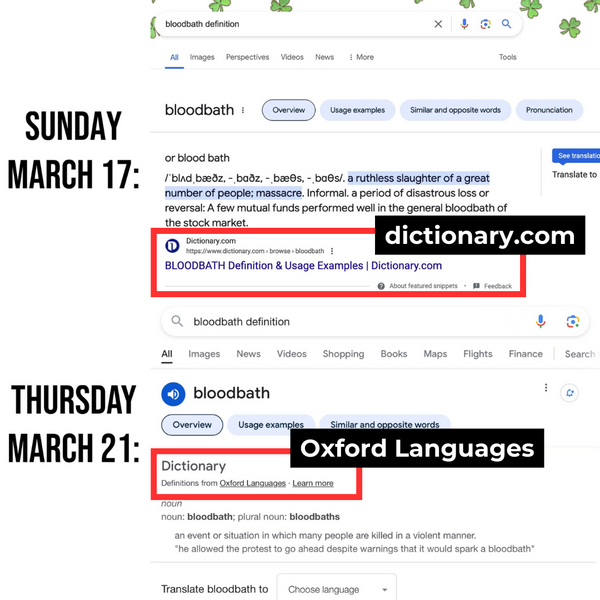
(X user @EndWokeness)
When we took a closer look at the viral image, we noticed the two screenshots were significantly different. The first one showed an “About featured snippets” caption, while the second one showed a “Dictionary, Definitions from Oxford Languages” legend. When we clicked on the “Oxford Languages” button, it redirected us to an Oxford Languages article, informing that “Google’s English dictionary is provided by Oxford Languages.”
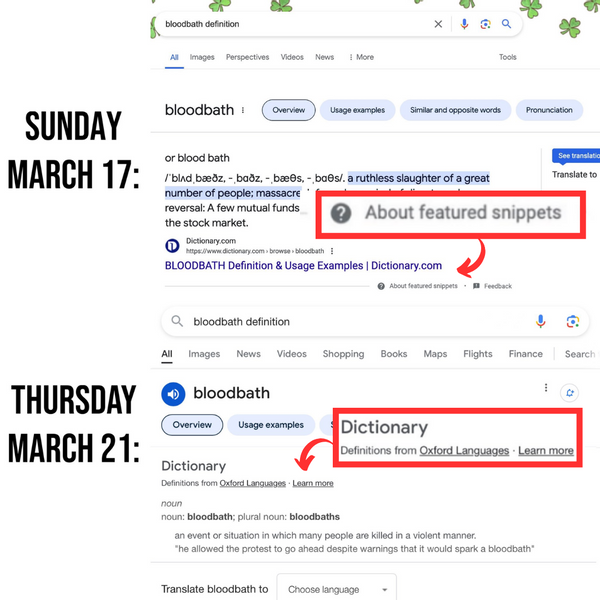
(X user @EndWokeness)
The first screenshot, allegedly captured on March 17, 2024, informed the displayed search result was a “featured snippet.” A Google Search Help article with the title “How Google’s featured snippets work” said that “Google’s search results sometimes show listings where the snippet describing a page comes before a link to a page, not after as with our standard format. Results displayed this way are called ‘featured snippets.'” It continued (emphasis ours):
You might find featured snippets on their own within overall search results, within the “People also ask” section, or along with Knowledge Graph information.
We display featured snippets when our systems determine this format will help people more easily discover what they’re seeking, both from the description about the page and when they click on the link to read the page itself. They’re especially helpful for those on mobile or searching by voice.
Featured snippets commonly contain one listing, but more than one may appear.
How featured snippets are chosen
Featured snippets come from web search listings. Google’s automated systems determine whether a page would make a good featured snippet to highlight for a specific search request. Your feedback helps us improve our search algorithms and the quality of your search results.
Ultimately, Google search results are based on many factors, such as one’s location or the phrasing of the query, which might cause differences in the search results over time:
To give you the most useful information, Search algorithms look at many factors and signals, including the words of your query, relevance and usability of pages, expertise of sources, and your location and settings. The weight applied to each factor varies depending on the nature of your query. For example, the freshness of the content plays a bigger role in answering queries about current news topics than it does about dictionary definitions.
We have fact-checked other Google-related rumors before. For instance, in June 2023, we investigated whether Google Maps was adding a feature that would allow drivers to challenge each other to a race. In January 2023, we debunked a false claim that a Google product designed to compete with Apple’s AirTag and Samsung’s SmartTag was named the “G-Spot.”
This article has been archived for your research. The original version from Snopes Fact Checks can be found here.



