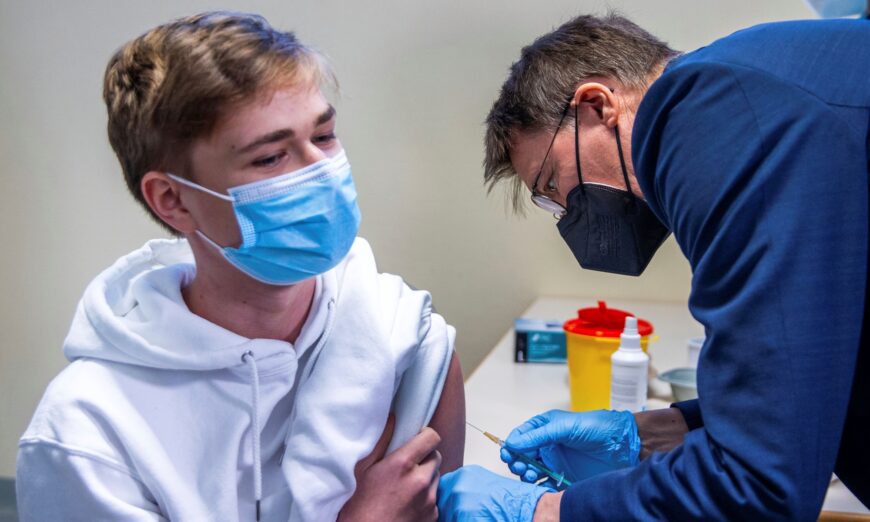
Sore Arm After COVID-19 Vaccine Could Indicate Serious Complication: Doctor
The arm pain is connected to heart-related conditions, which many experience after injecting the COVID vaccine.
Individuals who experience a sore arm after taking a COVID-19 shot may be at risk of facing cardiac issues, according to cardiologist Peter A. McCullough.
“The myocardial visual score was higher in patients who reported a sore arm compared with those who did not,” the study said. The participants in the study were “competitive and recreational athletes” from Italy.
Among the 460 participants in the study, 81.3 percent reported arm pain at the injection site after receiving the first dose of a COVID-19 shot. Following the second dose, 24.9 percent reported arm pain. “Male gender was more likely to present arm pain after the first and the second vaccinations,” it said.
“In our study population, arm pain was inversely associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection before vaccination.” Athletes who were previously infected with COVID-19 were found to be “less likely to present arm pain after the first-dose vaccination.”
Five individuals in the study received mRNA COVID-19 vaccines and died within a week of taking the shots. Four people died after the first injection, while the fifth died after the second dose.
In 80 percent of mRNA vaccine recipients, the study identified “acute (epi-)myocarditis without detection of another significant disease or health constellation that may have caused an unexpected death.”
The researchers discovered simultaneous vaccine-induced inflammation in the heart muscles and deltoid muscles crowning the shoulder. In the heart, the inflammation was found in the epicardium—the outermost protective layer of the organ located above the myocardium.
Cardiac Issues
Dr. McCullough also highlighted a December 2022 report published at the National Library of Medicine, which brought attention to the issue of rising cardiac arrests among athletes.
During a two-year period “from January 2021 to the time of writing, 1,598 athletes suffered cardiac arrest, 1,101 of which with deadly outcome,” it said, citing a study.
This is a higher rate of death compared to a 38‐year timespan between 1966 and 2004 when “1,101 athletes under the age of 35 died (~29/years) due to various heart‐related conditions.”
Citing another study on 301 teenagers between the ages of 13 and 18 who received two doses of the Pfizer vaccine, the report said “29.24 percent of participants experienced cardiovascular complications such [as] tachycardia, palpitations, and 2.33 percent suffered myopericarditis.”
“It is noteworthy that no statistically significant increase in the incidence of myocarditis or pericarditis was observed in un‐vaccinated subjects after SARS‐CoV‐2 infection, in a large population study.”
On the basis of these studies, Dr. McCullough determined that a sore arm can be a “harbinger of future cardiovascular serious adverse events.”
The cardiologist said that he was “amazed at how many people have taken one or more of the COVID-19 vaccines are completely free of side effects.” He suggested that many of the vials of the vaccine may have had “little or no viable mRNA.”
mRNA Toxicity
A study from Germany published in the British Journal of Pharmacology journal this month found that both Pfizer and Moderna’s mRNA COVID-19 vaccines formed spike proteins in the human heart cells within 48 hours of injection. Both Pfizer and Moderna triggered different cell abnormalities.
Responding to the study, Dr. McCullough suggested that the different responses the cells had to the two mRNA vaccines could point to an mRNA toxicity reaction in these cells.
Despite studies suggesting the risk of medical complications, some experts continue to advise people to get COVID-19 jabs. According to John Hopkins Medicine, both Pfizer and Moderna are “highly effective in preventing serious disease, hospitalization, and death from COVID-19.”
It recommended people to get a COVID-19 shot as “we believe that their benefits outweigh their risks.”